While choosing the right camera is a key factor for embedded vision applications, selecting the right lens plays just as important of a role in many of them. For instance, some applications require bandpass lenses to block a certain wavelength of light and allow the required wavelength of light to fall on the image sensor. As several bandpass lenses are available in the market, picking the right one depends on the unique requirements of your application.
For example, one of e-con Systems’ customers was developing a device that projects elements onto a surface using both visible and IR light. However, the camera monitoring the projected display should capture the IR data alone for the system’s algorithm to process. It proved to be a challenging decision to select the best-fit IR bandpass filter for their application. So, e-con Systems stepped in and closely worked with the customer before suggesting the absorption type IR filter for See3CAM_CU30 – low light USB camera from e-con Systems.
Now, let’s go in-depth and better understand the world of IR bandpass filters and lenses that use them.
What is an IR bandpass filter and lens?
IR bandpass lens allows only the IR light and blocks the remaining spectrum. If your application needs to capture only the IR light for processing, then you must choose the bandpass lens – depending on the IR wavelength used. And this is done by using what is called an IR bandpass filter. An IR bandpass filter uses a special optical glass coating, which allows only IR wavelength (usually NIR range from 780-1500nm) to pass through and blocks the visible wavelength (380nm to 700nm).
There are two types of IR filters, namely:
- Reflection type
- Absorption type
Reflection type IR filter
The reflection type infrared filter, also known as an optical cold mirror, is made on the optical white glass by vacuum coating. It reflects the visible light and allows infrared light to pass through. This infrared filter’s exterior looks similar to a mirror.

Figure 1 – a lens with reflection type IR filter
Absorption type IR filter
The absorption type IR filter usually has a black coating or is made up of black-colored glass. It absorbs the visible light and allows only the infrared light to fall on the sensor. It is important to note that the IR sensitivity of the absorption type infrared filter is higher than the reflection type.
 Figure 2 – a lens with absorption type IR filter
Figure 2 – a lens with absorption type IR filter
Transmission percentage of absorption & reflection type IR filters
In this section, let us look at the comparison of the transmission percentages (or percent transmission) of reflection type and absorption type IR filters. Transmission percentage is nothing but the ratio of the transmitted light intensity and the incident light intensity. The two images given below illustrate these values for both the types of IR filters:
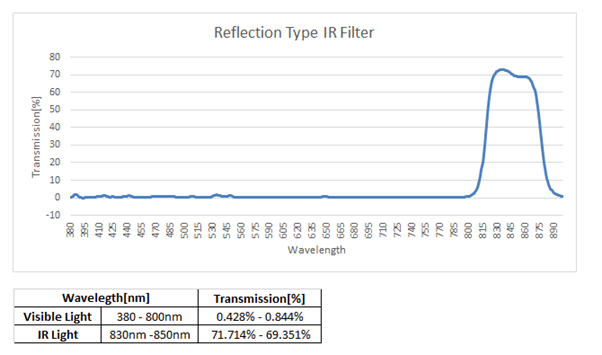
Figure 3 – transmission percetange of reflection type IR filter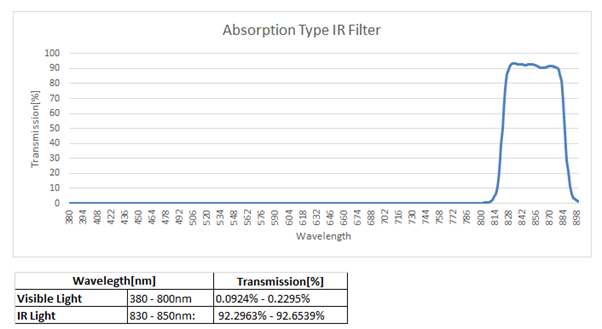 Figure 4 – transmission percentage of absorption type IR filter
Figure 4 – transmission percentage of absorption type IR filter
Upon comparing the data, you can see that the absorption type IR filter has higher IR sensitivity and blocks most of the visible light when compared to the reflection type IR filter. However, both of them are advantageous – with the absorption type IR filter used for use cases that need higher transmittance of IR and reflection type IR filter for lower transmittance.
Below are the comparison images captured using cameras with reflection type and absorption type lenses under visible light source alone:

Figure 5 – comparison of images taken with reflection and absorption IR filter lenses under a visible light source
From the above images, you can understand that the reflection type IR filter allows some range of visible light wavelengths, which explains why the images seem to be colored. But in the case of the absorption type IR filter, the visible light transmittance is very low and the IR transmittance very high. So, it blocks most of the visible light.
Now let us look at the same comparison when the light source is a combination of visible and IR light.
 Figure 6 – comparison of images taken with reflection and absorption IR filter lenses under a visible+IR light source
Figure 6 – comparison of images taken with reflection and absorption IR filter lenses under a visible+IR light source
In the above image, you can see that the IR light illumination is a lot more prominent in comparison with the visible light illumination – the images from both the IR filters look similar.
Key features of IR bandpass filters
- Superior blocking capabilities: IR bandpass filters excel at obstructing unwanted light from other spectral regions. It enhances the contrast and overall quality of the transmitted infrared light.
- Higher transmission efficiency: These filters help achieve high transmission rates within their designated wavelength range. It ensures the smooth passage of desired IR light.
- Selectivity of wavelengths: IR bandpass filters permit only a narrow spectrum of wavelengths. It effectively isolates specific IR bands for targeted applications.
- Thermal stability: These filters maintain their performance characteristics even under varying temperature conditions. So, they can be used in environments with fluctuating thermal profiles.
Embedded vision applications that need IR bandpass filters
Surveillance systems: In surveillance systems, IR bandpass filters boost night vision capabilities. By isolating specific infrared wavelengths, these filters improve image clarity and detail even in low-light conditions. It drives accurate monitoring and recording, which is crucial for security and surveillance operations.
Medical imaging devices: Infrared thermography cameras, for instance, use IR bandpass filters to isolate specific wavelengths for detailed tissue analysis. This isolation is important for accurate temperature measurement and diagnostics. Consequently, these filters also help use cases like patient monitoring and the early detection of medical conditions.
Smart agriculture systems: IR bandpass filters are used by drones and remote sensing equipment across many smart farming use cases. They help analyze crop health by isolating wavelengths that indicate plant stress, hydration levels, and chlorophyll content. Hence, farmers can make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, ultimately improving crop yield and health.
Biometric systems: In biometric systems, such as facial recognition and iris scanning technologies, IR bandpass filters increase the accuracy of capturing biometric data. They help filter out extraneous light, improving the contrast and detail of the images. It results in more reliable and secure biometric identification.
e-con Systems’ See3CAM_20CUG – a 2MP monochrome global shutter camera solution
e-con Systems is backed by 20+ years of experience in designing, developing, and manufacturing OEM cameras. We have customized numerous lens types, including IR bandpass lenses, for our clients.
We provide several camera solutions like See3CAM_20CUG – a powerful a 2MP global shutter monochrome USB 3.1 Gen 1 camera. This industrial USB camera is equipped with OmniVision’s 1/2.9″ OV2311 image sensor, which features 3μm x 3μm pixel OmniPixel® 3-GS technology. As a monochrome USB camera, it captures high frame rate images without motion blur, and its IR sensitivity ensures exceptional image quality even in Near Infrared (NIR) regions.
Visit the Camera Selector page to see our complete portfolio.
If you are looking for any help in integrating cameras into your product, please write to us at camerasolutions@e-consystems.com.

Vinoth Rajagopalan is an embedded vision expert with 15+ years of experience in product engineering management, R&D, and technical consultations. He has been responsible for many success stories in e-con Systems – from pre-sales and product conceptualization to launch and support. Having started his career as a software engineer, he currently leads a world-class team to handle major product development initiatives




